In recent years, the manufacturing industry has experienced a revolution with the rise of 3D printing technology. Specifically, 3D printing metal has emerged as an innovative and promising technique that is reshaping the future of manufacturing.
Let’s explore the advancements in 3D printing metal, also known as metal additive manufacturing, and discusses its impact on the industrial sector. From the benefits and applications to the potential it holds for the manufacturing revolution, we will delve into the exciting world of 3D printing metal and its role in the future of manufacturing.
The rise of 3D printing in the manufacturing industry
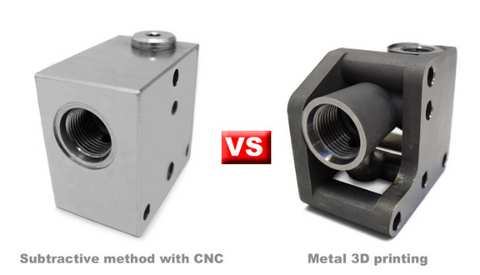
As the demand for customization and efficiency in manufacturing continues to grow, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology in the industry. The ability to print metal objects layer by layer using computer-aided design (CAD) models has opened a world of possibilities for manufacturers

One of the key advantages of 3D printing metal is its ability to reduce material waste. Traditional manufacturing processes often result in excess material being discarded, leading to inefficiencies and increased costs. With 3D printing metal, only the necessary amount of metal is used, minimizing waste and increasing cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, 3D printing metal allows for complex and intricate designs that were previously impossible to create with traditional manufacturing methods. This level of design freedom enables manufacturers to create highly customized and optimized metal products, improving functionality and performance.
Advancements in 3D printing metal
The field of 3D printing metal is constantly evolving, with new advancements being made to further improve the capabilities and applications of this revolutionary technology. Researchers and engineers are pushing the boundaries of what is possible, opening up a world of possibilities for manufacturers.

One area of advancement is the development of new materials for 3D printing metal. In addition to the traditional metals such as steel and aluminum, researchers are working on expanding the range of printable materials to include alloys and even precious metals. This opens up new opportunities for industries such as aerospace and jewelry, where high-performance and specialized metals are required.
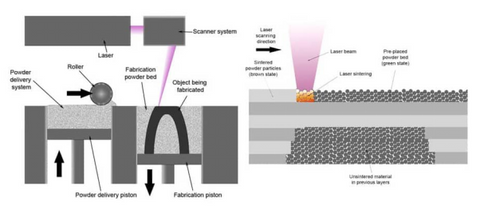
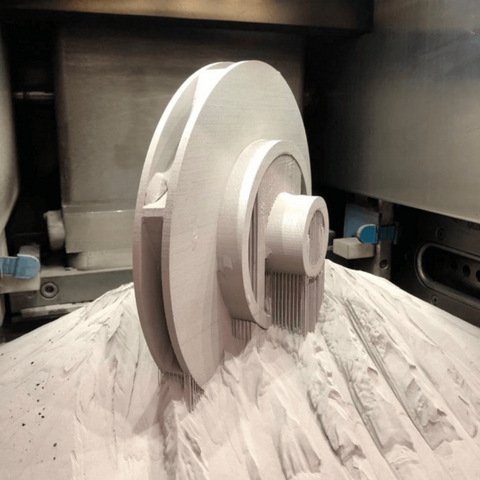
Another area of focus is improving the speed of 3D printing metal. While the technology has come a long way in terms of efficiency, there is still room for improvement. Researchers are working on developing faster printing processes and optimizing the design and manufacturing workflow to reduce production time.
Furthermore, advancements in software and design tools are making it easier for manufacturers to create complex and intricate designs for 3D printing metal. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms enables designers to optimize their designs for performance and efficiency, resulting in highly functional and customized products.
Benefits and limitations of using 3D printing metal
One of the primary advantages of 3D printing metal is its ability to create complex and intricate designs that were previously impossible or highly expensive to manufacture. Traditional manufacturing methods often require multiple steps, tooling, and assembly, but 3D printing metal can produce a single, fully functional part in one go, reducing the need for assembly and minimizing material waste.

Additionally, 3D printing metal offers design freedom, enabling manufacturers to create highly customized products tailored to specific needs. This flexibility allows for the production of unique, one-of-a-kind components, whether it be patient-specific medical implants or customized automotive parts, without the need for expensive molds or tooling.

However, like any technology, 3D printing metal has its limitations. One major constraint is the size of the printer itself. As of now, most 3D printers for metal are limited in size, which restricts the size of the parts that can be printed. Another limitation is the high cost of the equipment and materials required for 3D printing metal, making it less accessible to smaller manufacturers.
Additionally, the printing process can be time-consuming, especially for larger and more complex parts. While advancements are continually being made to improve printing speed, it is an area that still requires further development.
Industries adopting 3D printing metal
With its numerous benefits and advancements, it comes as no surprise that industries across the board are embracing 3D printing metal. A wide range of sectors are utilizing this technology to enhance their production capabilities and gain a competitive edge.
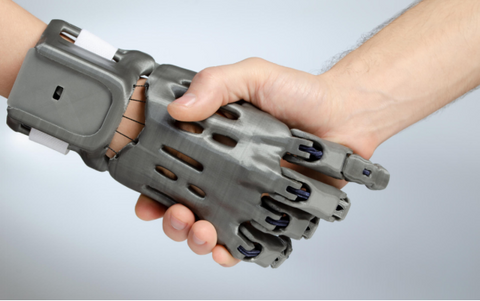
One industry that has greatly benefited from 3D printing metal is healthcare. Medical professionals can now create patient-specific implants and prosthetics, improving the precision and effectiveness of treatment. This technology also enables the production of complex medical devices, such as surgical instruments and dental implants, that require high degrees of customization.
The automotive industry is another sector that is rapidly adopting 3D printing metal. Manufacturers can create lightweight components, resulting in fuel-efficient vehicles without compromising on strength and safety. Additionally, customizing automotive parts to specific designs and requirements is now more feasible, allowing for greater innovation and personalization.
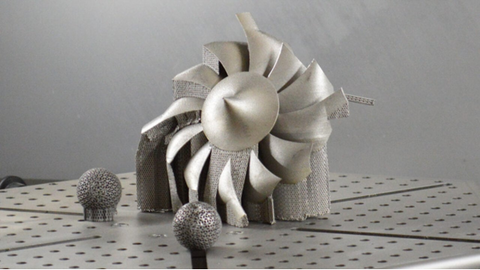
Aerospace is yet another industry where 3D printing metal is making significant strides. By employing this technology, manufacturers are able to produce complex and lightweight aircraft components, enhancing overall performance while reducing fuel consumption. The ability to create intricate designs that were previously unachievable has shaped the future of aerospace engineering.
The future of manufacturing with 3D printing metal
With the increasing adoption and advancements in 3D printing metal, the future of manufacturing looks incredibly promising. This transformative technology is set to revolutionize the entire production process across various industries. As we continue to explore the possibilities and push the boundaries of this technology, we can anticipate significant changes in how we manufacture goods.
One of the key areas where 3D printing metal is expected to have a major impact is in supply chain management. Traditional manufacturing often requires complex and lengthy supply chains, involving multiple suppliers and transportation logistics. With 3D printing metal, manufacturers have the ability to produce components on-demand, eliminating the need for extensive supply chains and reducing lead times. This not only saves time and money but also allows for more flexibility and agility in responding to market demands.
Furthermore, as the technology evolves, we can expect advancements in materials used for 3D printing metal. Currently, there are various metal alloys that can be 3D printed, each with its own unique properties and applications. In the future, we may witness the development of new materials specifically designed for 3D printing, with enhanced strength, durability, and heat resistance. This will open up new opportunities for manufacturing high-performance components that were previously unachievable.

Another area to watch out for is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in 3D printing metal technology. AI algorithms can analyze complex designs and optimize the printing process, minimizing errors and improving efficiency. Additionally, machine learning can help identify patterns and trends in the production data, allowing for continuous improvement and optimization of the printing process. This will lead to higher-quality products, reduced waste, and faster production times.
Embracing the potential of 3D printing metal in manufacturing
In conclusion, the potential of 3D printing metal in manufacturing is something that cannot be overlooked. As we have seen, this transformative technology is already making a significant impact on the industry, and the future looks even more promising. The ability to produce components on-demand, reduced lead times, and increased flexibility in responding to market demands are just a few of the benefits that 3D printing metal brings to the table.
Undoubtedly, the future of manufacturing with 3D printing metal is bright. As more industries recognize the immense potential and continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, we can expect to witness a revolution in how we produce goods. Exciting times lie ahead, and those who embrace this transformative technology will be well-positioned for success in the future.
FAQ
1.Q: What advantages does 3D printing metal offer in comparison to traditional manufacturing processes?
A: 3D printing metal provides benefits such as reduced material waste, the ability to create intricate designs, and increased cost-effectiveness by using only the necessary amount of metal, addressing inefficiencies associated with traditional manufacturing.
2.Q: How is the field of 3D printing metal advancing, and what are the current areas of focus for researchers and engineers?
A: Researchers and engineers are actively working on developing new materials for 3D printing metal, expanding beyond traditional metals to include alloys and precious metals. There is also a focus on improving printing speed, optimizing design tools, and integrating artificial intelligence to enhance the capabilities and applications of this transformative technology.
3.Q: What are the limitations of 3D printing metal, and are there ongoing efforts to overcome these challenges?
A: The limitations of 3D printing metal include the size constraints of printers, high equipment and material costs, and time-consuming printing processes, especially for larger and more complex parts. Ongoing efforts in research and development aim to address these challenges, with a focus on enhancing printing speed, reducing costs, and expanding the range of printable materials.
4.Q: In which industries is 3D printing metal finding significant applications, and how does it benefit these sectors?
A: Industries such as healthcare, automotive, and aerospace are actively adopting 3D printing metal. In healthcare, the technology is used for patient-specific implants and prosthetics, while in the automotive industry, it enables the creation of lightweight components for fuel-efficient vehicles. In aerospace, 3D printing metal is revolutionizing the production of complex and lightweight aircraft components, improving overall performance and fuel efficiency.